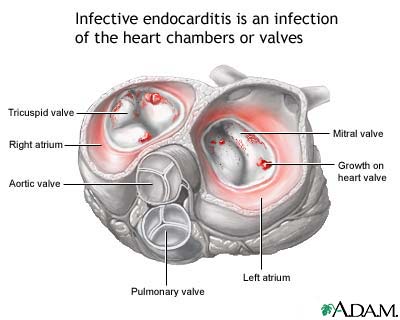
Endocarditis is the infection of the endocardial suface of the heart including the valves. Most people who develop endocarditis have underlying valvular heart disease. The disease due to rheumatic heart disease, prostatic heart valve, IV drug use, mitral valve prolapsed, and infection by bacteria (Streptococci, Enterococci, or Staphylococcus aureous). Infective endocarditis has a 20-30% mortality rate.
Endocarditis can be diagnosed by positive blood cultures and presence or valvular vegetations on echocardiogram.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Anorexia
- Malaise
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Night sweats
- Heart murmurs
- Wight loss
- Elevated ESR and WBC
Treatments:
- Antibiotic to eliminate all microorganism and prevent complication
- Surgical repair or replacement of damaged valves.
Nursing Interventions:
- Assess and monitor vital signs and heart sound (the presence of murmurs)
- Administer IV antibiotics as prescribed
- Monitor for side effects of antibiotic (renal or ototoxicity)
- Assess and monitor signs of heart failure, embolic event, or dysrhythmias
- Provide adequate rest
- Teach patient to avoid recurrence of infections
- Teach patient to avoid excessive fatigue and to stop activities that result in chest pain, faintness, or dyspnea
- Teach patient the importance of completing medication schedule and side effects of medication




0 comments:
Post a Comment