Coronary artery disease is a condition in which one or more coronary arteries become narrowed or obstructed. It can be result from atherosclerosis and an accumulation of lipid-containing plague in arteries. This condition causes decreases perfusion of myocardial tissue and inadequate myocardial oxygen supply. The goal of treatment is to alter the atherosclerotic progression.
Coronary artery disease leads to hypertension, angina, dysrhythmias, myocardial infarct, heart failure, and death.
Coronary artery narrowing is significant if the lumen diameter of the left main artery is reduced at least 50% or if any major branch is reduced at least 75%.
Sign and Symptoms Coronary Artery Disease:
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Dyspnea
- Syncope
- Excessive fatigue
- Cough or hemoptysis
- Possibly normal findings during asymptomatic
Diagnostic Procedure for Patient with Coronary Artery Disease:
- Electrocardiogram: ST segment depression or T wave inversion when blood flow is reduced and ischemia occurs. ST segment elevation followed by T wave inversion when infarction occurs.
- Cardiac Catheterization: It will show the presence of atherosclerotic lesions.
- Blood Lipid Levels: may be elevated.
Nursing Interventions:
- Inform patient regarding the purpose of diagnostic medical and surgical procedures
- Assist and identify risk factors that can be modified
- Instruct the patient regarding a low-calorie, low sodium, los cholesterol, and low fat diet with an increase in dietary fiber
- Inform the patient that dietary changes are not temporary but maintained for life
- Instruct the patient regarding prescribed medications
- Instruct the patient regarding exercise, smoking reduction, and stress reduction
Surgical Procedures for Coronary Artery Disease:
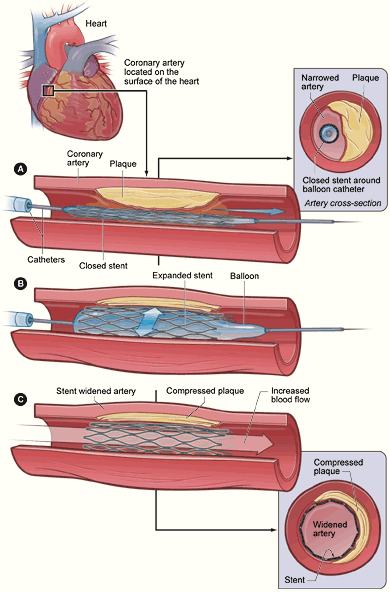
- PTCA: to compress the plaque against the wall of the artery and dilate the vessel
- Laser angioplasty: to vaporize the plaque
- Vascular stent: to prevent the artery from closing and to prevent restenosis
- Atherectomy: to remove the plaque from the artery
- Coronary artery bypass graft: to improve blood flow to the myocardial tissue
Medications
- Nitrates: to dilate the coronary arteries and to decrease preload and afterload
- Cholesterol-lowering medications: to reduce the development of atherosclerotic plaques
- Calcium channel blockers: to dilate coronary arteries and reduce vasospasm
- Beta blocker: to reduce blood pressure





0 comments:
Post a Comment