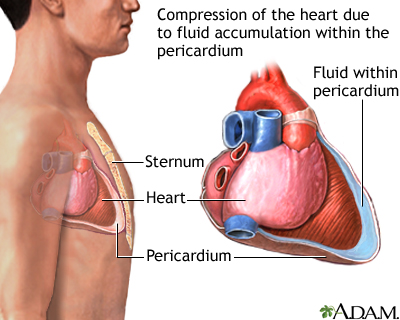
Cardiac tamponade is compression of the heart due to critically increased volume of fluid in the pericardium. The space between the parietal and visceral layers of the pericardium are filled with fluid. Acute cardiac tamponade occurs when small volume (20-50 ml) of fluid accumulate in the pericardium.
Cardiac tamponade will restrict ventricular filling and cardiac output drops.
Signs and Symptoms of Cardiac Tamponade:
- Pulsus paradoxus
- Jugular venous distention with clear lungs
- Increased CVP
- Distant, muffled heart sounds
- Cardiac output is decreased
Intervention for Cardiac Tamponade:
- Place patient in a critical care unit for hemodynamic monitoring
- Administer fluid intravenously as prescribed
- Prepare patient for chest x-ray, echocardiogram, and pericardiocentesis (to draw pericardial fluid) if prescribed




0 comments:
Post a Comment